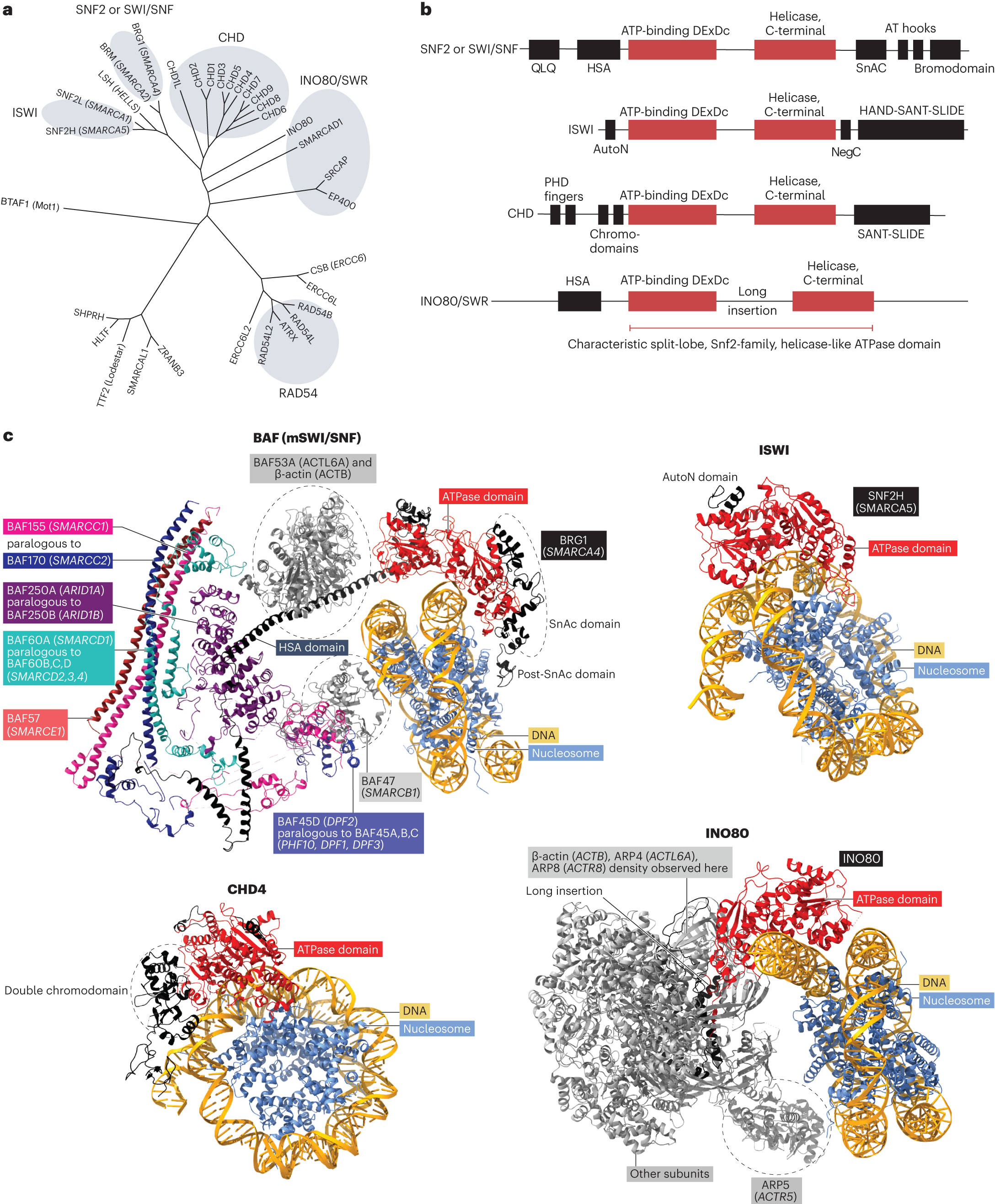
Context-specific functions of chromatin remodellers in development and disease
By A Mystery Man Writer

Chromatin is changed during aging. (1) Younger cells contain

ARID1A - Wikipedia

β-actin dependent chromatin remodeling mediates compartment level changes in 3D genome architecture

Context-specific functions of chromatin remodellers in development

Chromatin remodelling in mammalian differentiation: lessons from

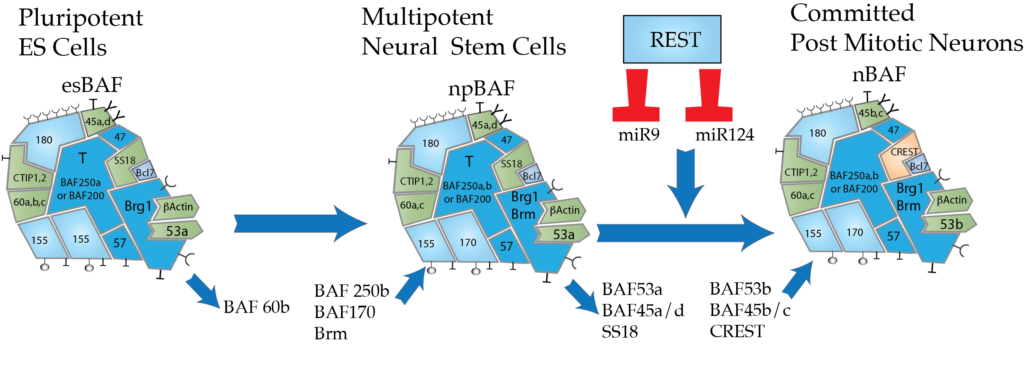
Chromatin crosstalk in development and disease: lessons from REST
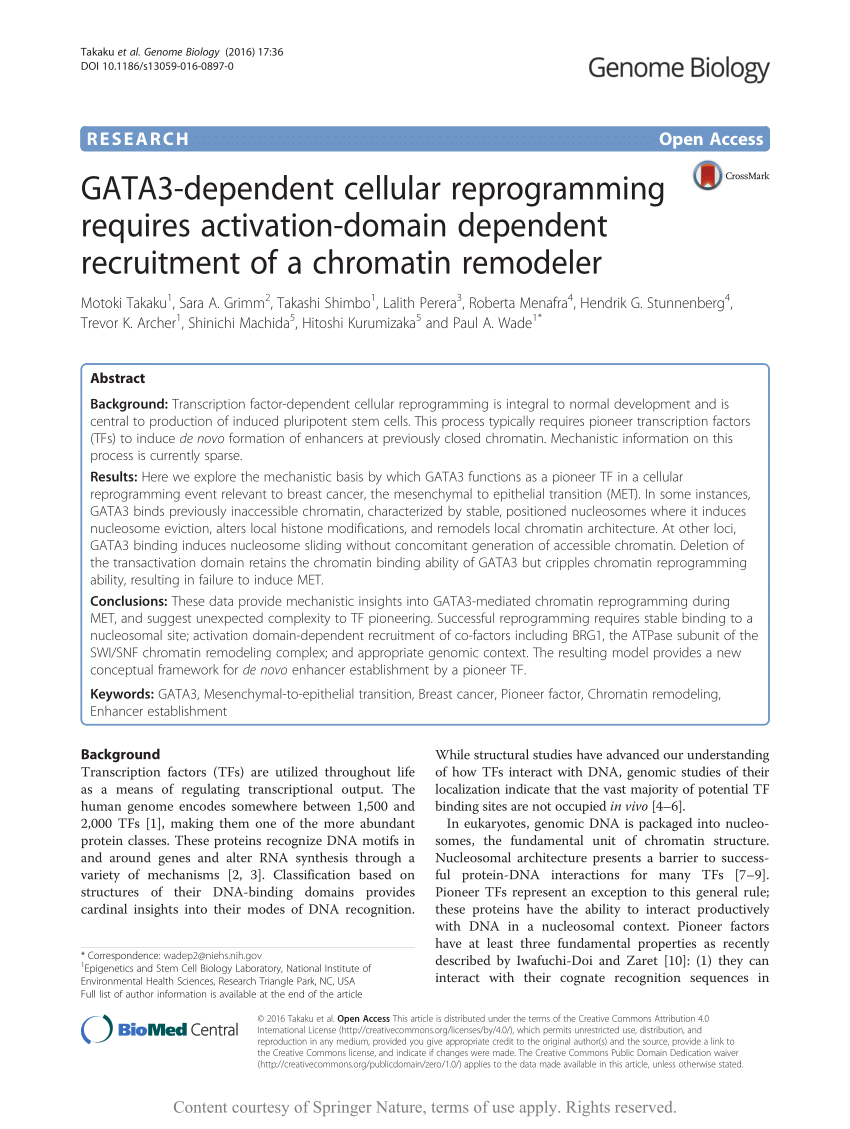
PDF) GATA3-dependent cellular reprogramming requires activation-domain dependent recruitment of a chromatin remodeler
Understanding the Words of Chromatin Remodeling – Crabtree

Chromatin Remodeling - an overview

PDF] Unwinding chromatin at the right places: how BAF is targeted to specific genomic locations during development

ATP-dependent chromatin remodeling during mammalian development. - Abstract - Europe PMC
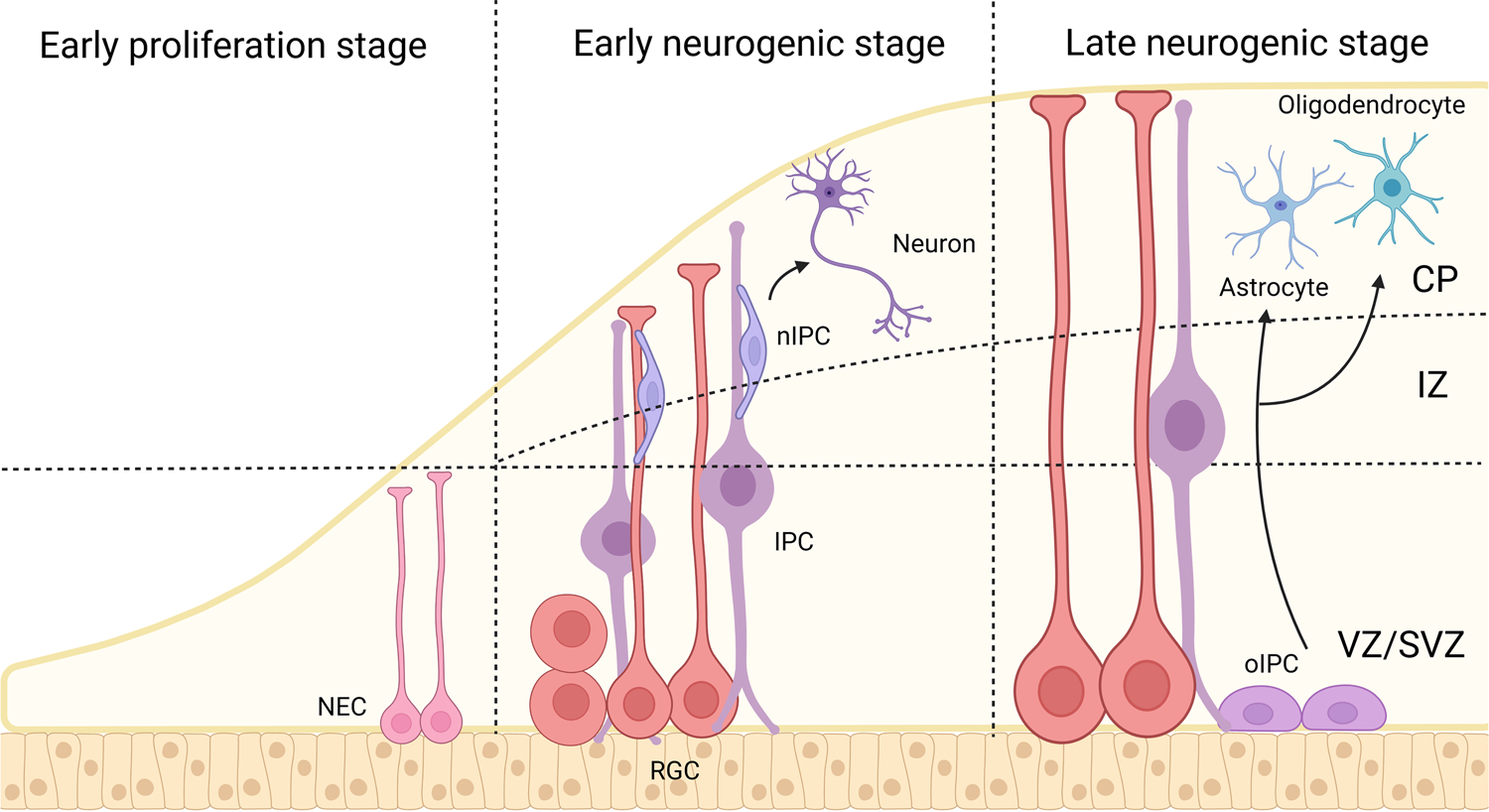
The role of histone modifications: from neurodevelopment to

Chromatin Remodeling in Eukaryotes